题目:Long Wavelength Laser based on Semiconductor Broken-Gap Heterostructures
报告人:赵光安 教授(瑞典Lund大学教授)
摘要:
Since more than 15 years ago when I worked on semiconductor heterostructures, I have been bothered by the problem that a quantum well can not emit a photon with energy less than its energy gap. I came across the following picture: I draw the energy diagram of a quantum well, cut it into two parts at the middle of well, and then shift the left part vertically with respect to the right part. If the new resulting quantum well can emit photons via the transition of electrons from the conduction band at the left to the valence band at the right, the photon energy can be lower than the energy gap of the original quantum well. Soon after I realized that my imaginary quantum well can be fabricated with broken-gap heterostructure in which the quantum well is made with InAs/GaSb.
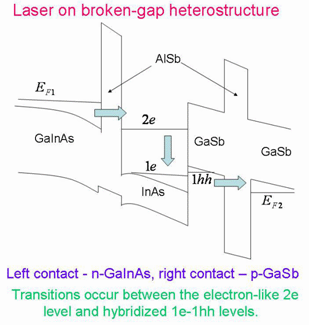
While I was excitedly working on this project of long wavelength laser and started to cooperate with materials scientists, I learned that the carrier injecting process requires much complicated heterostructures. Even worse, I found out that in order to understand the physical properties of carriers in this complicated sample in which the lattice mismatch induced strain depends on the sample growth-process, one must take into account the effects of electron-hole hybridization and various symmetry breaking mechanisms such as structural inversion asymmetry, bulk inversion asymmetry, and interface Hamiltonian.
It took me more than ten years to complete the theoretical study of this problem, during which I also discovered that wavelength of the emitted light can be tuned with an applied magnetic field. I will explain to you the relevant physics of my suggested laser structure as shown in the following figure.








